November 18th, 2005 — 12:00am
In the overview of the new “results oriented” UI planned for MS Office 12, our friends in Redmond offer:
“The overriding design goal for the new UI is to deliver a user interface that enables users to be more successful finding and using the advanced features of Microsoft Office. An additional important design goal was to preserve an uncluttered workspace that reduces distraction for users so that they can spend more time and energy focused on their work.”
Let me get that straight. Your first goal is to make it easier for me to find and use advanced features that the vast majority of people employ rarely if ever, and didn’t need in the first place?
And something else that was also important – but not as important as access to all those shiny advanced features – was to make the workspace uncluttered and allow me to focus on my work?
Isn’t that… backwards?
Related posts:
Comment » | User Experience (UX)
November 17th, 2005 — 12:00am
I got caught in an on-line opinion survey trap last week. The setup: In exchange for 10% off my next purchase, a Banana Republic cashier told me, I had to answer a few questions about my shopping experience. Retailers often solicit opinions from customers in return for a variety of rewards. It’s common enough that there’s an understanding on the amount of information requested, in exchange for the expected reward. So I thought I was safe…
Twenty screens later, after answering more than fifty questions and with no end in sight, I was feeling a little cranky. Even my wife was irritated; I was holding up grocery shopping for dinner guests. Very quickly, the reward for my time shifted from a coupon, to using Banana Republic as an example of an on-line survey experience that undermines your brand.
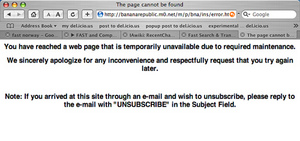
The full survey ran more than thirty five screens, and ended with an error message. Very professional.
Thumbnails of the whole survey:
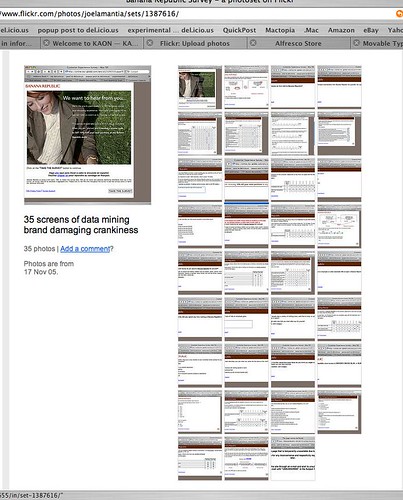
For kicks, I posted the screenshots to Flickr. If you run the slideshow, you can see where I became frustrated and started to give spoiler answers – like wearing a size 98, or spending $10 / year on clothing.
Why was the survey experience bad?
1. They didn’t make clear how much time they were asking for. The opening screen said 10 minutes, this is misleading for a 100 question survey. If you’re asking for my time, respect me enough to be honest about what’s required.
2. They didn’t make the real purpose of the survey clear. From the shopping experience itself, the questions quickly shifted to my age, income, marital status, and education level. This is a transparent attempt to feed data mining and demographic needs that relied on an amateur segue to turn the conversation around and ask for personal information.
3. They contradicted the experience I had in their store. The store staff were nice enough to keep track of the umbrella I left in a fitting room, and return it before I left, which was thoughtful. Consistency is the core of a successful brand, but the survey experience was inconsistent.
How does this damage Banana Republic’s brand?
1. Banana Republic left me with a series of negative impressions that work against their brand values: I now feel I was chosen to participate in a survey under false pretenses, a survey that offers me little value in return for important personal information that is inappropriate to ask for in the first place.
2. Banana Republic closed a growing channel for conducting business with a customer. I may purchase more from their stores — if I have no other retailer at hand, and I need business clothes to meet with a client CEO the next morning once again — but I’m certainly not willing to engage with them online.
Merchants in all areas of retailing work very hard to encourage customers to form positive associations with their brands. Fashion retailers work especially hard at encouraging customers to associate values, such as trust and respect, with a brand because these values serve as the foundation for longer term and more lucrative relationships with customers than single purchases. Every experience a customer has with your brand — every touch point — influences this network of associations, reinforcing or weakening the link between a brand and the feelings that customers have about the products and the company behind it. A simple test any retailer should use when considering bringing an experience to customers is wether the experience will reinforce the right brand associations.
Loyalty programs, and their offspring the online opinion survey, are good examples of the intersections of customer interests and retailer interests in an experience that can reinforce a customer’s perceptions of the brand and the values associated with it. Many retailers manage these kinds of programs well.
Just not Banana Republic.
The error message at the end.
Error Message:
I wear size 98:
Size 98:

Related posts:
Comment » | User Experience (UX)
November 17th, 2005 — 12:00am
At least according to the Boston Globe article titled Don’t underestimate the value of social skills, in which Penelope Trunk quotes an HBS faculty member as follows:
’In fact, across the board, in a wide variety of businesses, people would rather work with someone who is likable and incompetent than with someone who is skilled and obnoxious, said Tiziana Casciaro, a professor at Harvard Business School. “How we value competence changes depending on whether we like someone or not,” she says.‘
I guess this explains how we ended up with George W. Bush as President…
No related posts.
Comment » | The Working Life
November 4th, 2005 — 12:00am
A few months ago, I put up a posting on Mental Models Lotus Notes, and Resililence. It focused on my chronic inability to learn how not to send email with Lous Notes. I posted about Notes, but what led me to explore resilience in the context of mental models was the surprising lack of acknowledgement of the scale of hurricane Katrina I came across at the time. For example, the day the levees failed, the front page of the New York Times digital edition carried a gigantic headline saying ‘Levees Fail! New Orleans floods!’. And yet no one in the office at the time even mentioned what happened.
My conclusion was that people were simply unable to accept the idea that a major metropolitan area in the U.S. could possibly be the setting for such a tragedy, and so they refused to absorb it – because it didn’t fit in with their mental models for how the world works. Today, I came across a Resilience Science posting titled New Orleans and Disaster Sociology that supports this line of thinking, while it discusses some of the interesting ways that semantics and mental models come into play in relation to disasters.
Quoting extensively from an article in The Chronicle of Higher Education titled Disaster Sociologists Study What Went Wrong in the Response to the Hurricanes, but Will Policy Makers Listen? the posting calls out how narrow slices of media coverage driven by blurred semantic and contextual understandings, inaccurately frame social responses to disaster situations in terms of group panic and the implied breakdown of order and society.
“The false idea of postdisaster panic grows partly from simple semantic confusion, said Michael K. Lindell, a psychologist who directs the Hazard Reduction and Recovery Center at Texas A&M University at College Station. ‘A reporter will stick a microphone in someone’s face and ask, ‘Well, what did you do when the explosion went off?’ And the person will answer, ‘I panicked.’ And then they’ll proceed to describe a very logical, rational action in which they protected themselves and looked out for people around them. What they mean by ‘panic’ is just ‘I got very frightened.’ But when you say ‘I panicked,’ it reinforces this idea that there’s a thin veneer of civilization, which vanishes after a disaster, and that you need outside authorities and the military to restore order. But really, people usually do very well for themselves, thank you.’
Mental models come into play when the article goes on to talk about the ways that the emergency management agencies are organized and structured, and how they approach and understand situations by default. With the new Homeland Security paradigm, all incidents require command and control approaches that assume a dedicated and intelligent enemy – obviously not the way to manage a hurricane response.
“Mr. Lindell, of Texas A&M, agreed, saying he feared that policy makers in Washington had taken the wrong lessons from Katrina. The employees of the Department of Homeland Security, he said, ‘are mostly drawn from the Department of Defense, the Department of Justice, and from police departments. They’re firmly committed to a command-and-control model.’ (Just a few days ago, President Bush may have pushed the process one step further: He suggested that the Department of Defense take control of relief efforts after major natural disasters.)
“The habits of mind cultivated by military and law-enforcement personnel have their virtues, Mr. Lindell said, but they don’t always fit disaster situations. ‘They come from organizations where they’re dealing with an intelligent adversary. So they want to keep information secret; ‘it’s only shared on a need-to-know basis. But emergency managers and medical personnel want information shared as widely as possible because they have to rely on persuasion to get people to cooperate. The problem with putting FEMA into the Department of Homeland Security is that it’s like an organ transplant. What we’ve seen over the past four years is basically organ rejection.’
If I read this correctly, misaligned organizational cultures lie at the bottom of the whole problem. I’m still curious about the connections between an organization’s culture, and the mental models that individuals use. Can a group have a collective mental model?
Accoridng to Collective Mental State and Individual Agency: Qualitative Factors in Social Science Explanation it’s possible, and in fact the whole idea of this collective mental state is a black hole as far as qualitative social research and understanding are concerned.
Related posts:
Comment » | Modeling, The Media Environment
November 3rd, 2005 — 12:00am
Apparently, if you wait long enough, all circles close themselves. Case in point: I’ve always thought Golding’s Lord of the Flies nicely captures several of the less appetizing aspects of the typical american junior high school experience.
And I’ve always thought that much of the reality television programming that was all the rage for a while and now seems to be passing like a Japanese fad, is simply a chance for people on all sides of the screen to revisit their own junior high school experiences once again — albeit with a full complement of adult secondary sexual characteristics. When I do channel surf past the latest incarnation of the primal vote-the-jerk-off-the-island epic, Golding’s book always comes to mind.
Then a friend recommended Koushun Takami’s Battle Royale as recreational reading. Battle Royale is, as Tom Waits says, ‘big in Japan’ – it being a Japanese treatment of some of the same themes that drive Lord of the Flies.
The editorial review from Amazon reads:
“As part of a ruthless program by the totalitarian government, ninth-grade students are taken to a small isolated island with a map, food, and various weapons. Forced to wear special collars that explode when they break a rule, they must fight each other for three days until only one “winner” remains. The elimination contest becomes the ultimate in must-see reality television.”
And so the circle closes…
Related posts:
Comment » | Reading Room, The Media Environment

